In the ever-evolving world of education, one of the most essential tasks for teachers and administrators is identifying and addressing students’ learning gaps. Understanding the specific areas where a student is struggling allows educators to tailor instruction and interventions to better meet each student’s individual needs. One of the most effective tools used to measure these learning gaps is the nwea map scores by grade level 2025 (Measures of Academic Progress) test.
What is the NWEA MAP?
The NWEA MAP is a standardized assessment tool that measures a student’s academic growth in key subject areas, including math, reading, language usage, and science. Unlike traditional tests that provide a static snapshot of student performance, the MAP test is adaptive, meaning the questions adjust in difficulty based on the student’s responses. This dynamic approach helps ensure that the test is appropriate for students at all levels, allowing educators to get a clear picture of both strengths and weaknesses.
NWEA MAP assessments are typically given multiple times throughout the academic year—usually in the fall, winter, and spring—so teachers can track progress and growth over time. By providing detailed insights into where students stand in their learning journey, the MAP test helps identify both individual learning gaps and broader trends across classes, schools, and districts.
How the NWEA MAP Identifies Learning Gaps
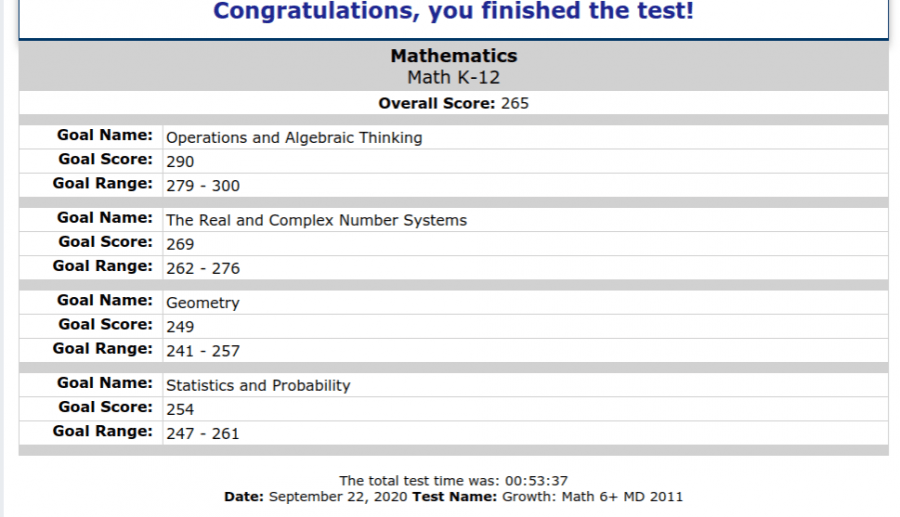
One of the primary benefits of the NWEA MAP test is its ability to identify specific learning gaps at both the individual and group levels. The test provides data that is broken down into precise areas of knowledge, enabling educators to pinpoint exactly where a student may be struggling.
1. Pinpointing Areas of Struggle
When a student takes the MAP test, the system generates a score known as the RIT (Rasch unIT), which reflects the student’s current level of academic understanding. This score is not tied to age or grade level, which is particularly useful because it gives a more accurate picture of a student’s academic ability. The RIT score can be mapped onto specific learning targets, such as reading comprehension or algebraic reasoning, allowing educators to identify where a student’s skills may be lacking.
For example, a student who consistently struggles with fractions in math will show a lower RIT score in that area compared to other areas of math, such as basic arithmetic or geometry. The data provides clear evidence that targeted instruction in fractions is necessary to help that student advance.
2. Measuring Growth Over Time
Another critical aspect of the NWEA MAP test is its ability to track a student’s growth. By taking the test at multiple points during the year, educators can compare a student’s current score to their previous results. This provides a clear indication of academic progress, helping teachers determine whether a student is catching up, staying on track, or falling further behind.
For instance, a student who shows significant improvement from the fall to the spring may no longer have the same gaps in their learning, whereas a student whose scores have remained stagnant could need additional support. The MAP test gives teachers actionable data that can inform decisions about whether a student is ready for more challenging material or if they require additional interventions.
3. Informing Instructional Decisions
One of the most effective ways to use MAP data is by leveraging it to make informed instructional decisions. The test’s ability to provide granular information on specific learning standards means that teachers can design lessons that address the unique needs of their students.
For example, if a class of students shows an overall weakness in understanding cause and effect in reading, the teacher can adjust their curriculum to include targeted lessons that emphasize those skills. By using the MAP scores to inform instruction, teachers can close learning gaps more efficiently and ensure that all students are receiving the support they need.
The Benefits of Identifying Learning Gaps with NWEA MAP
The ability to identify and address learning gaps is crucial to ensuring that all students achieve academic success. The NWEA MAP test provides several benefits in this process.
1. Personalized Learning
By identifying specific areas of struggle, the NWEA MAP allows for a more personalized approach to teaching. Teachers can tailor lessons to individual students, offering extra practice and support in areas where the student needs it most. This personalized attention helps students feel supported and engaged, which is essential for improving academic outcomes.
2. Timely Interventions
Because the MAP test is administered multiple times a year, teachers have the ability to intervene early if a student begins to show signs of falling behind. If a student shows a decline in performance, immediate interventions can be implemented—whether through targeted one-on-one sessions, small group instruction, or adjustments to the curriculum. Early interventions are often key to preventing students from falling further behind and becoming discouraged.
3. Data-Driven Decision Making
The detailed data provided by the NWEA MAP test empowers educators to make data-driven decisions, rather than relying solely on subjective judgment. With the insights provided by the test, educators can focus their efforts on areas that are most likely to yield the greatest impact, ensuring that their time and resources are being used effectively.
Conclusion
In the quest to provide high-quality education for all students, identifying and addressing learning gaps is critical. The NWEA MAP test plays a vital role in this process by providing accurate, actionable data that helps educators understand where their students are excelling and where they need additional support. By using MAP data to inform instruction and interventions, educators can ensure that every student has the opportunity to succeed academically, ultimately leading to improved educational outcomes for all.